Hi everyone! In this article I will be writing on how to set up a completely free Technical SEO Audit Web-App via using Google Sheets and Google Apps Script. In this way you’ll be able to detect critical errors immediately or on a weekly, monthly basis depending on how you decide to set up the system. This setup will also be beneficial if you do not have access to paid SEO tools such as Ahrefs, Semrush or Screaming Frog as the Google Apps Script is a cloud-based scripting language tool that is completely free to use and it can run as a web-app for maximum efficiency and accessibility.
To get started, you’ll need a Google account and a basic understanding of Google Sheets. Follow these steps to create your own Technical SEO Audit App Script:
Setting up Google Sheets and Apps Scripts
To create a spreadsheet in Google Sheets, you can follow these steps:
- Open Google Sheets:
- Open your web browser and sing in to Google if you have not already
- By entering “https://sheets.new/” you can easily create a spreadsheet.
- Activate Apps Script
- Click Extensions and then choose App Script
- A new tab will be opened and you can give a name to your project
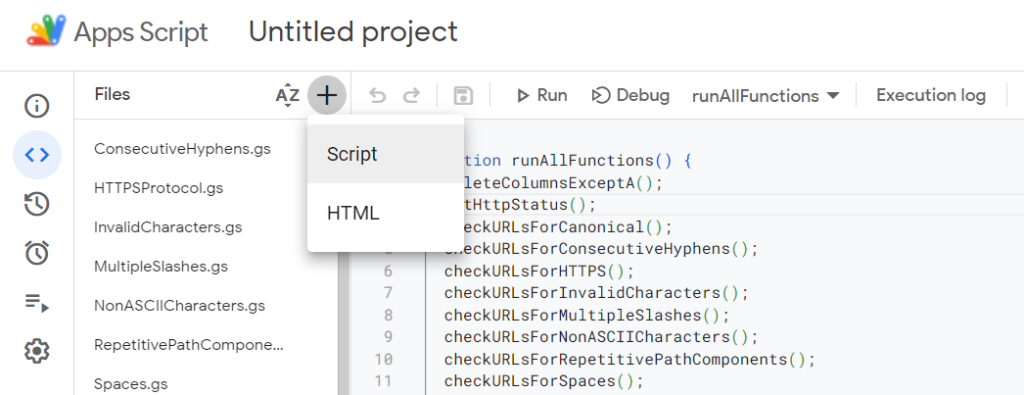
How to Add Scripts to Google Apps Script
Adding a script is a fairly easy process. All you need to do is to click ‘+’ symbol in the Files tab and choose ‘Script’ and then you can give a name to your script here. Because our first script will be to retrieve URLs from our sitemap we will name our first script as “getSitemapURLs” as it is the name of the function in the code
You can access to the Javascript code for getSitemapURLs here: getSitemapURLs
The important thing to pay attention in this case is to replace the sitemap link in the code with the sitemap link you want to retrieve URLs from. Make sure to save the code and run it when you make any changes. However, if you want to use various URLs independent of any sitemap you can skip adding this code and add the URLs you desire in column A.
Adding & Running All of the SEO Scripts
Now that you know how to create new scripts I will be giving a list of all the JavaScript codes and what their function is. You can decide to add some of these codes to your App Script Workspace.
Let’s start with retrieving URLs from the sitemap.
getSitemapURLs()
Purpose: This function helps you gather all the website URLs listed in the sitemap and puts them into the Column A of the Google Sheets document.
How It Works:
- You specify the web address of your sitemap.
- The function fetches the sitemap’s content.
- It organizes the sitemap’s content.
- The function clears any existing data in the Google Sheets document.
- Finally, it loads all the URLs from the sitemap into the Google Sheets document.
In a nutshell, this function automates the process of collecting and storing website URLs from your sitemap in a Google Sheets document, making it easier for you to collect URLs existing in the sitemap.
deleteColumnsExceptA()
Purpose: This function deletes all columns in a Google Sheets document except for the first column (Column A).
Usage: This function is used to clean up the sheet by removing all of the columns, keeping only the data in the first column (Column A). In this way you can clean up the data from the previous executions.
getHttpStatus()
Purpose: This function checks the HTTP status of URLs in a Google Sheets document and adds the results in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and data range of Column A
- Adds an “HTTP Status” header in the next empty column.
- For each URL, it checks the HTTP response code:
- “3xx redirect” for redirects.
- “✓” for successful requests (2xx).
- “X” for other cases.
- “Broken Page” for errors (4xx-5xx).
Usage: Helps identify broken links and redirects, providing an overview of URL health for SEO auditing.
checkURLsForCanonical()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they have a canonical tag and if the canonical tag is self-referential, and records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “URLs without Canonical Tag” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and performs the following steps:
- Fetches the HTML content of the URL.
- Checks if the HTML content contains a canonical tag
<link rel="canonical". - If a canonical tag is found, it extracts the canonical URL from the tag.
- Compares the canonical URL with the original URL to check if it’s self-referential.
- Marks “✓” (checkmark) if the URL has a self-referential canonical tag.
- Marks “Non Self-Referential Canonical Tag” if the canonical tag points to a different URL.
- Marks “Canonical Tag Missing” if no canonical tag is found.
- Marks “Error” if there’s an error during the fetch (e.g., URL fetch failure).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps identify URLs without canonical tags, URLs with non-self-referential canonical tags, and URLs with self-referential canonical tags. Canonical tags are important for SEO to specify the preferred version of a URL.
checkURLsForH1Tags()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they have H1 tags and records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “H1 Tags” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and performs the following steps:
- Fetches the URL content and counts the number of H1 tags (
<h1>) in the page. - If there are no H1 tags, it marks “Missing H1 Tag.”
- If there are multiple H1 tags, it marks “Multiple H1 Tags.”
- If there’s exactly one H1 tag, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- If there’s an error during the fetch (e.g., URL fetch failure), it marks “Error.”
- Fetches the URL content and counts the number of H1 tags (
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps identify URLs with missing or multiple H1 tags, which can affect SEO and content structure. It ensures proper usage of H1 tags for better SEO optimization.
checkURLsForRepetitivePathComponents()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain repetitive path components and records the results in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “Repetitive Path Components” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and checks for repeated path components.
- It splits the URL path by ‘/’ and removes any empty strings.
- It then checks if there are repeated path components using a Set data structure.
- If repetitive path components are found, it marks “Contains repetitive path components.”
- If not, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Repetitive URL Path Example: (.com/red/automobile/red/)
Usage: This function helps identify URLs with repetitive path components, which can impact SEO and user experience negatively. It ensures URLs have a cleaner and more structured path.
checkURLsForConsecutiveHyphens()
Purpose: This function identifies URLs in a Google Sheets document that have consecutive hyphens (–) and records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “Consecutive Hyphens” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL, checking for consecutive hyphens using a regular expression.
- If consecutive hyphens are found, it marks “Consecutive Hyphens.”
- If not, it marks “✓” (checkmark) indicating no consecutive hyphens.
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps spot URLs with consecutive hyphens, which can impact SEO negatively, ensuring a cleaner and more SEO-friendly URL structure.
checkURLsForHTTPS()
Purpose: This function checks URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify whether they use the HTTPS protocol and records the results in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “HTTPS Protocol” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL, checking if it starts with “https://”.
- If it starts with “https://”, it marks “✓” (checkmark) indicating HTTPS.
- If not, it marks “Missing HTTPS protocol.”
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps ensure that URLs are using the secure HTTPS protocol, which is important for both user security and SEO rankings. It identifies URLs that do not use HTTPS, allowing you to address any security and SEO concerns.
checkURLsForInvalidCharacters()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain invalid characters in the URL path, and records the results in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “Invalid Characters in URL Path” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and extracts the URL path component.
- Applies a regular expression pattern to check for valid characters in the path:
- If the path contains invalid characters, it marks “Invalid characters in the URL path.”
- If the path is valid, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps ensure that URLs have valid characters in their paths, which is essential for proper functionality and SEO compatibility. It identifies URLs with problematic characters, allowing you to address issues that could affect SEO and user experience.
checkURLsForMultipleSlashes()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain multiple consecutive slashes and records the results in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Adds a “Multiple Slashes” header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL to check if it starts with “https://” and contains two or more consecutive slashes using a regular expression.
- If the URL has multiple consecutive slashes, it marks “Contains multiple slashes.”
- If not, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps detect URLs with excessive consecutive slashes, which can negatively impact SEO and user experience. It ensures URLs follow best practices for clean and consistent URL structure.
checkURLsForNonASCIICharacters()
Purpose: This function checks URLs in a Google Sheets document for non-ASCII characters and records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- Fetches the active sheet and data range.
- Adds “Non-ASCII Characters” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL, using the
isASCII()helper function to check for non-ASCII characters.- If non-ASCII characters are found, it marks “Non-ASCII Characters Found.”
- Otherwise, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: Identifies URLs with non-ASCII characters, ensuring compatibility across systems and browsers for SEO and user experience.
checkURLsForSpaces()
Purpose: This function checks URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain spaces and records the results in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “URLs with Spaces” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and checks if it contains spaces using the
indexOf()method.- If spaces are found in the URL, it marks “Contains Spaces.”
- If not, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps detect URLs with spaces, which can negatively impact SEO and user experience. It ensures URLs follow best practices by eliminating spaces.
checkURLsForURLStructure()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they have incorrect URL structures and records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “URL Structure Issues” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and checks if it matches a predefined URL structure pattern using a regular expression.
- If the URL structure doesn’t match the pattern, it marks “Incorrect URL structure.”
- If it matches, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps identify URLs with incorrect structures, ensuring that URLs follow a standardized pattern for better SEO and user experience.
checkURLsForUnderscores()
Purpose: This function checks URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain underscores and records the results in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “URLs with Underscores” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and checks if it contains underscores using the
indexOf()method.- If underscores are found in the URL, it marks “Contains Underscores.”
- If not, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps detect URLs with underscores, which can negatively impact SEO and user experience. It ensures URLs follow best practices by eliminating underscores.
checkURLsForUppercaseChars()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain uppercase characters and records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “Uppercase Characters” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and checks if it contains uppercase characters using a regular expression.
- If uppercase characters are found in the URL, it marks “Contains Uppercase Characters.”
- If not, it marks “✓” (checkmark).
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps detect URLs with uppercase characters, which can impact SEO negatively and affect consistency. It ensures URLs follow best practices by using lowercase characters.
checkForHreflangTags()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain <link> elements with hreflang attributes and records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “Hreflang Tags” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and performs the following steps:
- Fetches the HTML content of the URL.
- Uses a regular expression to find
<link>elements withhreflangattributes. - If
<link>elements withhreflangattributes are found, it marks “✓” (checkmark). - If no such elements are found, it marks “Missing Hreflang Tags.”
- If there’s an error during the fetch (e.g., URL fetch failure), it marks “Error.”
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps identify URLs that are missing <link> elements with hreflang attributes, which are essential for international SEO and content localization. It ensures that the necessary hreflang tags are correctly implemented for SEO optimization.
checkURLsForNoIndex()
Purpose: This function examines URLs in a Google Sheets document to identify if they contain a <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> tag, which indicates that a page should not be indexed by search engines. The function records the findings in a new column.
Functionality:
- It fetches the active sheet and the data range.
- Determines the next empty column.
- Adds “Indexability” as a header in the next empty column.
- Iterates through each URL and performs the following steps:
- Fetches the HTML content of the URL using
UrlFetchApp. - Uses a regular expression to find
<meta>tags with anameattribute set to “robots” and acontentattribute containing “noindex” (case-insensitive). - If such a
<meta>tag is found, it marks “NoIndex Tag.” - If no such tag is found, it marks “✓” to indicate that the page is indexable.
- If there’s an error during the fetch (e.g., URL fetch failure), it marks “Error.”
- Fetches the HTML content of the URL using
- Records the results in the next empty column.
Usage: This function helps identify URLs that contain a <meta name="robots" content="noindex"> tag, which instructs search engines not to index the page. It’s essential for SEO analysis and ensures that web pages are correctly configured for search engine visibility.
sendEmail()
Purpose: This function sends an email containing a PDF SEO report generated from the data in the Google Sheets document.
For this code you should replace the email address with your own email address.
Functionality:
- It gets the active spreadsheet and its first sheet.
- Defines a range that includes all the data in the sheet.
- Creates a PDF blob from the spreadsheet.
- Sets the email subject as ‘SEO PDF Report.’
- Constructs the email body with a link to the Google Sheets document and a message.
- Specifies the recipient’s email address (replace with your email address).
- Sends the email with the PDF report attached.
Usage: This function automates the process of sending SEO reports as PDF attachments via email, making it easy to share the audit results with others.
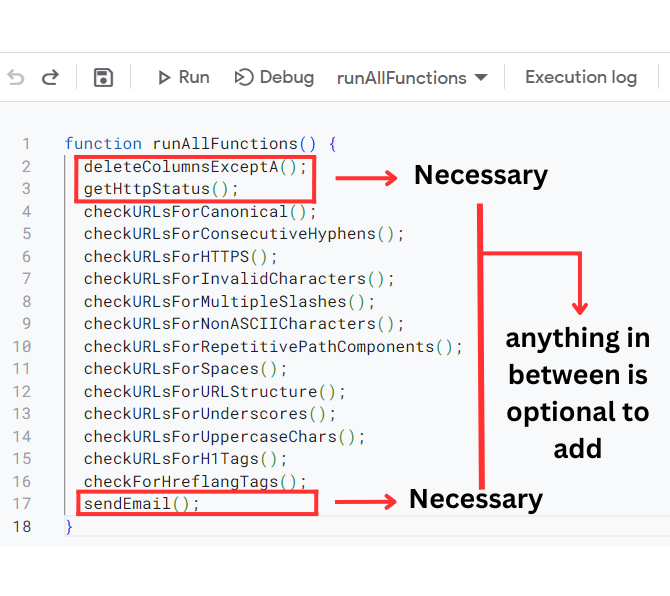
How to Run All of the Functions at Once
You do not have to add each of these scripts. However, if you do intend to run all of those scripts then it may be difficult to run each of these code one by one or add a trigger for each one of these codes to run. Also Google Apps Script triggers are limited to only 20. In order to be more productive and bypass the 20 trigger limit you can add the following function as a script:
function runAllFunctions() {
getSitemapURLs();
deleteColumnsExceptA();
getHttpStatus();
checkURLsForConsecutiveHyphens();
checkURLsForRepetitivePathComponents();
checkURLsForH1Tags();
checkForHreflangTags();
checkURLsForCanonical();
checkURLsForHTTPS();
checkURLsForInvalidCharacters();
checkURLsForMultipleSlashes();
checkURLsForNonASCIICharacters();
checkURLsForSpaces();
checkURLsForURLStructure();
checkURLsForUnderscores();
checkURLsForUppercaseChars();
checkURLsForNoIndex();
sendEmail();
}
In order to add more of these functions you can just insert the function name and add (); at the end of it. Alternatively, you can remove any of these codes that you do not want to execute. The most important thing here is that the hierarchical order. This is because the runAllFunctions code runs according to the hierarchy meaning that whichever code is at the top it will run first. Based on this execution hierarchy, we must add getSitemapURLs first if we want to retrieve URLs from a sitemap and then deleteColumnsExceptA so that we can remove the data from the previous reports and the last of the function in the hierarchy should be sendEmail as it is supposed to send us the reports of the latest version of the sheet.
How to Add a Trigger in Google Apps Scripts
Adding a trigger in Google Apps Script allows you to automate the execution of a script at a specific time or in response to an event. Therefore, in order to set up our system we should then add a trigger.
- Set Up a Trigger:
- Click on the clock icon (
Triggers) in the left-hand sidebar of the Google Apps Script editor. This will open the triggers page.
- Click on the clock icon (
- Add a Trigger:
- Click the “+ Add Trigger” button appearing in the bottom right. This will open a dialog where you can configure the trigger settings.
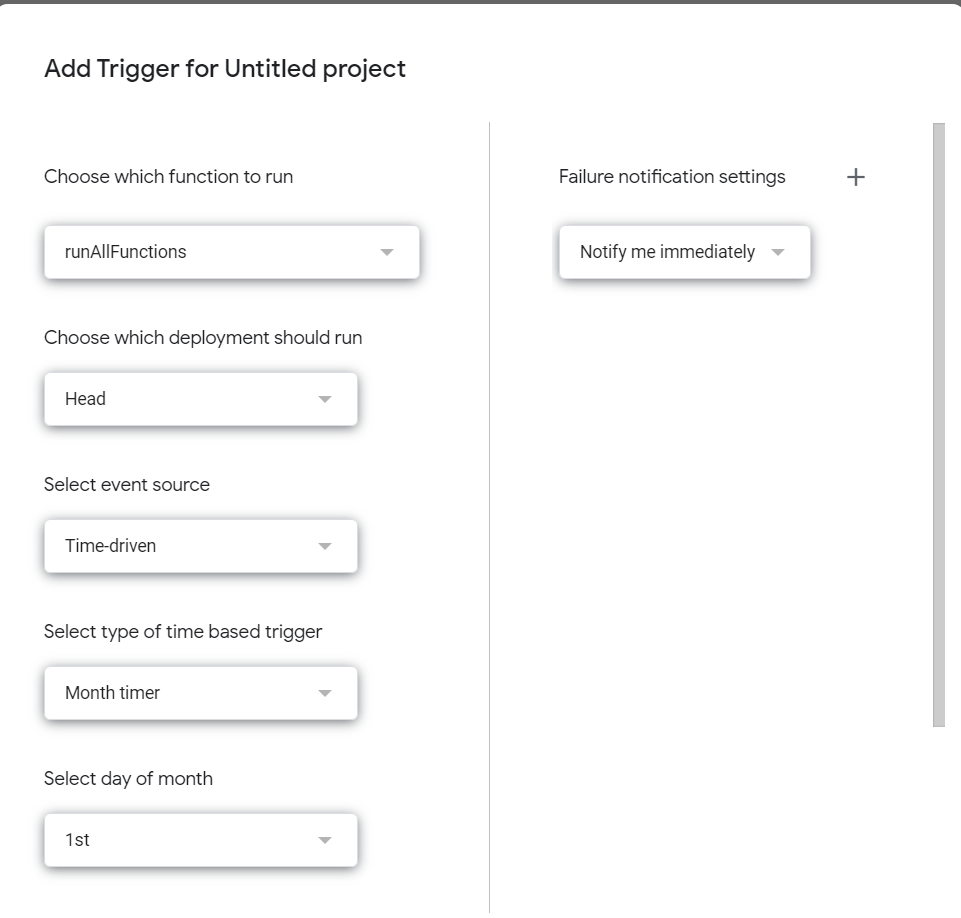
- Choose ‘runAllFunctions’ as the trigger function
- In this way you’ll be able to execute all functions with one trigger
- Configure Trigger Settings
- Select ‘Time-Driven’ as the event source
- You should decide on the level of frequency you intend to run this project whether it be daily, weekly, monthly etc.
- Opt ‘Notify me Immediately’ for the Failure notification settings and save the trigger.
Deploying the SEO Audit Project
Now that we’ve set our scripts as well as our trigger now we can deploy our project. Click ‘Deployment’ in the top right and choose ‘New deployment’. For the configuration you should choose ‘Web-App’ and then save. With this deployment you will then receive automatic SEO Audit reports and keep your website up-to-date!
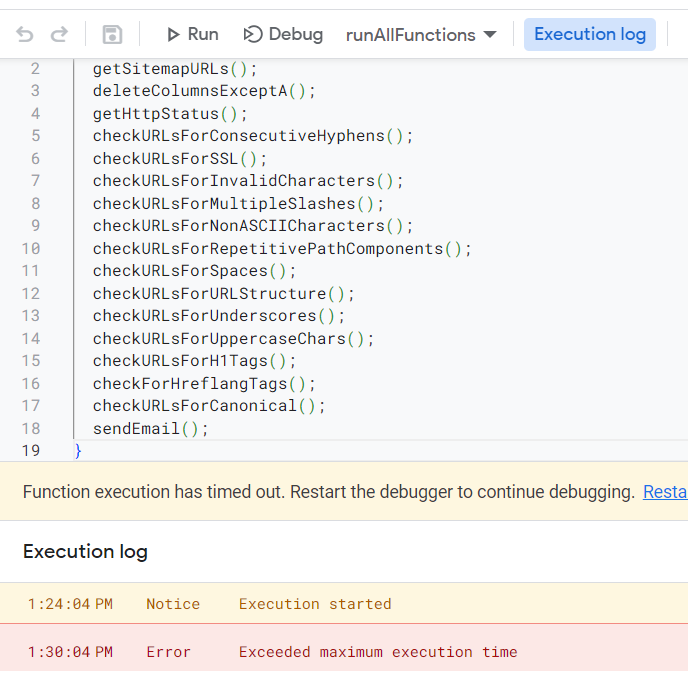
Google Apps Script Limitations
Although Google Apps Scripts is a completely free cloud-based scripting language and offers free web-app service it is important to mention that the time limit of the execution of runAllFunctions is 6 minutes. This means that if it takes longer than 6 minutes to execute the projects due to the number of URLs or other reasons then it will not finish the code. In order to prevent this you can divide the scripts in the runAllFunctions to two or three seperate runAllFunctions and set seperate triggers paying extra attention to the hierarchical structure of the codes. Alternatively you can divide the URLs into different sheets and create seperate SEO reports for these URLs.
See more for the limitations:
https://developers.google.com/apps-script/guides/services/quotas
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve shown how to create a free Technical SEO Audit App Script using Google Sheets and Google Apps Script. This system allows you to automate critical SEO checks, even if you don’t have access to paid SEO tools.
By setting up this script, you can efficiently identify and address technical SEO issues, ensuring your website performs well in search results. With the ability to schedule regular audits, you’ll keep your website in top shape for optimal user experience and search engine ranking.
Just be mindful of time limitations for larger websites. Consider dividing tasks or optimizing your setup to stay within the execution time constraints.
In summary, this DIY approach empowers you to take control of your website’s technical SEO, all without the expense of premium SEO tools. Improve your online visibility and organic traffic by implementing these strategies today.


